Foundation Forms - custom control renderers
You can create custom control renderers to work alongside the standard set of foundation form controls.
This page guides you through the steps. You need to create a renderer class and a control rank. You then register the custom renderer in your template.
Examples
Custom renderer template
You need to create a custom renderer template to render your new form control. This example creates a control that renders options using the Segmented Control element.
export const SegmentedControlRendererTemplate= () => html<DispatchRenderer>`
<template>
<control-wrapper
:control=${(x) => x.control}
:touched=${(x) => x.touched}
?submitted=${(x) => x.submitted}
>
<rapid-segmented-control
@change=${(x, c) => {
x.control.handleChange(
x.control.path,
(c.event.target as any).value
);
x.onBlur();
}}
>
${repeat((x, ctx) => x.control.uischema.options.data, html`
`)}
</rapid-segmented-control>
</control-wrapper>
</template>
`
The template contains the segmented control element and uses the repeat directive to iterate over the options provided in the UISchema, setting the value attribute on each item and the label value in each item's slot.
The template listens to the @change event and calls the handleChange event on the DispatchRenderer to set the value in the form.
The template then calls onBlur to indicate the form has been touched.
Control renderer
Next, create an object that matches the RendererEntry interface. We need three properties:
rendererwhich returns aViewTemplateusing thehtmlfunction. This will return theSegmentedControlRendererTemplatewe created above.testerwhich uses therankWithfunction. This takes two params - a control rank (a number) and a function which returns a truthy value. If true, it returns the specified number. The default renderer rank is two, so ensure your rank value is higher than that.mapperwhich is a function to map form state to control props. We use themapStateToControlPropsfrom json-forms here.
const SEGMENTED_CONTROL_RANK = 5;
export const SegmentedControlRenderer: RendererEntry = {
renderer: html`${SegmentedControlRendererTemplate}`,
tester: rankWith(SEGMENTED_CONTROL_RANK, (args) => {
return args.options?.segmented;
}),
mapper: mapStateToControlProps,
}
Invoking the custom renderer
The last step to enable you to use your new custom renderer is to register it with foundation-forms and give the right config so that the form class knows to render it.
In creating your UiSchema, remember that the tester function is checking if segmented is set in the options of the UISchemaElement.
rankWith(SEGMENTED_CONTROL_RANK, (args) => {
return args.options?.segmented;
})
So in the UISchema, define with the value set in the options.
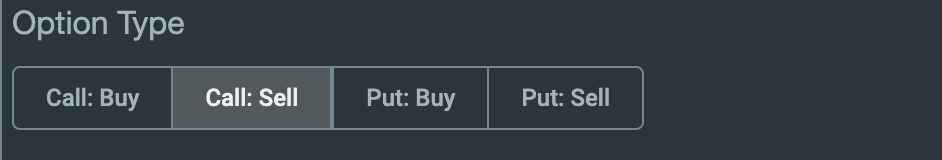
const optionTypes = [
{ value: 'CallBuy', label: 'Call: Buy' },
{ value: 'CallSell', label: 'Call: Sell' },
{ value: 'PutBuy', label: 'Put: Buy' },
{ value: 'PutSell', label: 'Put: Sell' }
];
export const segmentedControlUIElement: UiSchemaElement = {
type: 'Control',
scope: '#/properties/optionType',
options: <ConnectedRenderersOptions>{
segmented: true,
data: optionTypes
}
};
export const formsWithCustomRenderersUISchema: UiSchema = {
type: 'VerticalLayout',
elements: [
segmentedControlUIElement,
...
]
}
Then in your template, pass your uischema configured with a segmented control and set the renderers attribute to include your custom renderer in addition to the standard set of foundation forms renderers.
import { SegmentedControlRenderer } from './segmented-control-renderer';
import { renderers } from '@genesislcap/foundation-forms';
...
<foundation-form
:renderers="${() => [...renderers, SegmentedControlRenderer]}"
design-system-prefix="rapid"
:uischema="${() => formsWithCustomRenderersUISchema}"
:jsonSchema="${() => formsWithCustomRenderersJsonSchema}"
>
</foundation-form>
If everything is working, you should see your new Segmented Control custom renderer.
After you have looked at the basics here, you can find more details in our API Docs
Full source code at Custom Controls