Foundation Forms JSON schema
Foundation forms use a JSON Schema to define the underlying model of the form. This defines the objects and properties, as well as their types.
If the source of the data is a resource in a Data Server or Event Handler of your application, then you can use the JSON schema that is generated automatically by the Genesis Platform. Alternatively, you can define your own schema on the client.
This section covers aspects of the Data Server and DataBase sections. The examples provided are simple, but it is worth exploring these sections in more depth.
Examples
Server-side JSON schema
Here is an example of a simple table defined in an application's -tables-dictionary.kts file. It is a simple table with three fields:
smart-forms-examples-tables-dictionary.kts
tables {
table(name = "SIMPLE_TRADE", id = 10_000) {
field("SIMPLE_TRADE_ID", STRING).sequence("ST")
field("QUANTITY", DOUBLE)
field("SIDE", STRING)
primaryKey("SIMPLE_TRADE_ID")
}
...
}
The data for this table is provided by a query in the application's -dataserver.kts file. This is the data source:
smart-forms-examples-dataserver.kts
dataServer {
query("ALL_SIMPLE_TRADES", SIMPLE_TRADE)
...
}
The event that enables you to insert the data from the form into the database table is provided in the application's -eventhandler.kts file. This is the data source:
smart-forms-examples-eventhandler.kts
eventHandler {
eventHandler<SimpleTrade>("SIMPLE_TRADE_INSERT", transactional = true) {
onCommit { event ->
val details = event.details
entityDb.insert(details)
ack()
}
}
...
}
...
To insert the automatically-generated JSON schema for this resource into your template file, use the code below:
- Genesis
- React
- Angular
Declaration:
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="EVENT_TRADE_INSERT"
></foundation-form>
Usage:
@customElement({
name: 'form-example',
template: html`
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="EVENT_TRADE_INSERT"
></foundation-form>
`,
})
export class FormExample extends GenesisElement {}
Declaration:
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="EVENT_TRADE_INSERT"
></foundation-form>
Usage:
export default function FormExample({}) {
return (
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="EVENT_TRADE_INSERT"
></foundation-form>
);
}
Declaration
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="EVENT_TRADE_INSERT"
></foundation-form>
Usage
import { Component, CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'my-root',
template: `
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="EVENT_TRADE_INSERT"
></foundation-form>
`,
standalone: true,
schemas: [CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA],
imports: [FormsModule],
})
export class AppComponent {}
Once you have done this, you will see a form that looks like this:
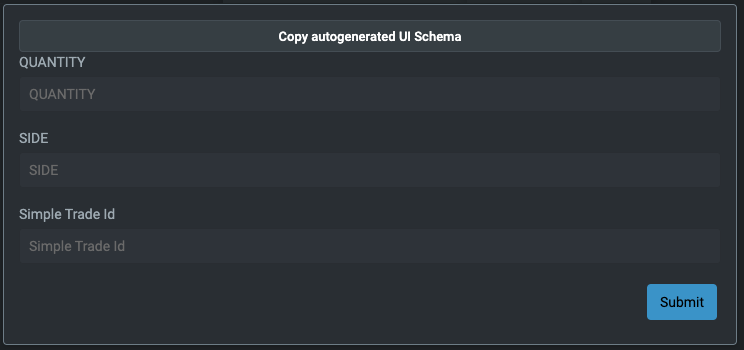
Client-side JSON schema
You can create your own JSON schema on the client side if you want to specify the exact content layout of the form.
Here is an example of a JSON schema defined on the client. It describes an object with two properties - QUANTITY and SIDE, similar to the one we described above.
You set the JSON schema on the foundation-form element using the jsonSchema attribute.
The resulting form looks similar but it has no id field:
- Genesis
- React
- Angular
Declaration:
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
:jsonSchema="${() => sampleJsonSchema}"
></foundation-form>
Usage:
const sampleJsonSchema = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
QUANTITY: {
type: 'number',
description: 'kotlin.Double',
},
SIDE: {
type: 'number',
description: 'kotlin.String',
},
},
};
@customElement({
name: 'form-example',
template: html`
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
:jsonSchema="${() => sampleJsonSchema}"
></foundation-form>
`,
})
export class FormExample extends GenesisElement {}
Declaration:
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
jsonSchema={sampleJsonSchema}
></foundation-form>
Usage:
const sampleJsonSchema = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
QUANTITY: {
type: 'number',
description: 'kotlin.Double',
},
SIDE: {
type: 'number',
description: 'kotlin.String',
},
},
};
export default function FormExample({}) {
return (
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
jsonSchema={sampleJsonSchema}
></foundation-form>
);
}
Declaration
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
[jsonSchema]="jsonSchema"
></foundation-form>
Usage
import { Component, CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
const sampleJsonSchema = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
QUANTITY: {
type: 'number',
description: 'kotlin.Double',
},
SIDE: {
type: 'number',
description: 'kotlin.String',
},
},
};
@Component({
selector: 'my-root',
template: `
<foundation-form
design-system-prefix="rapid"
[jsonSchema]="jsonSchema"
></foundation-form>
`,
standalone: true,
schemas: [CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA],
imports: [FormsModule],
})
export class AppComponent {
jsonSchema = sampleJsonSchema;
}
After you have looked at the basics here, you can find more details in our API Docs
Full source code at JSON/UI Schema example.