Custom Elements LSP
The Custom Elements LSP plugin enables you to use your LSP-enabled editor with IntelliSense handling for web-component custom elements. This gives you warnings and errors, autocompletion, diagnostics, and jump-to definition as you work on your Genesis project.
For example, attribute completion:
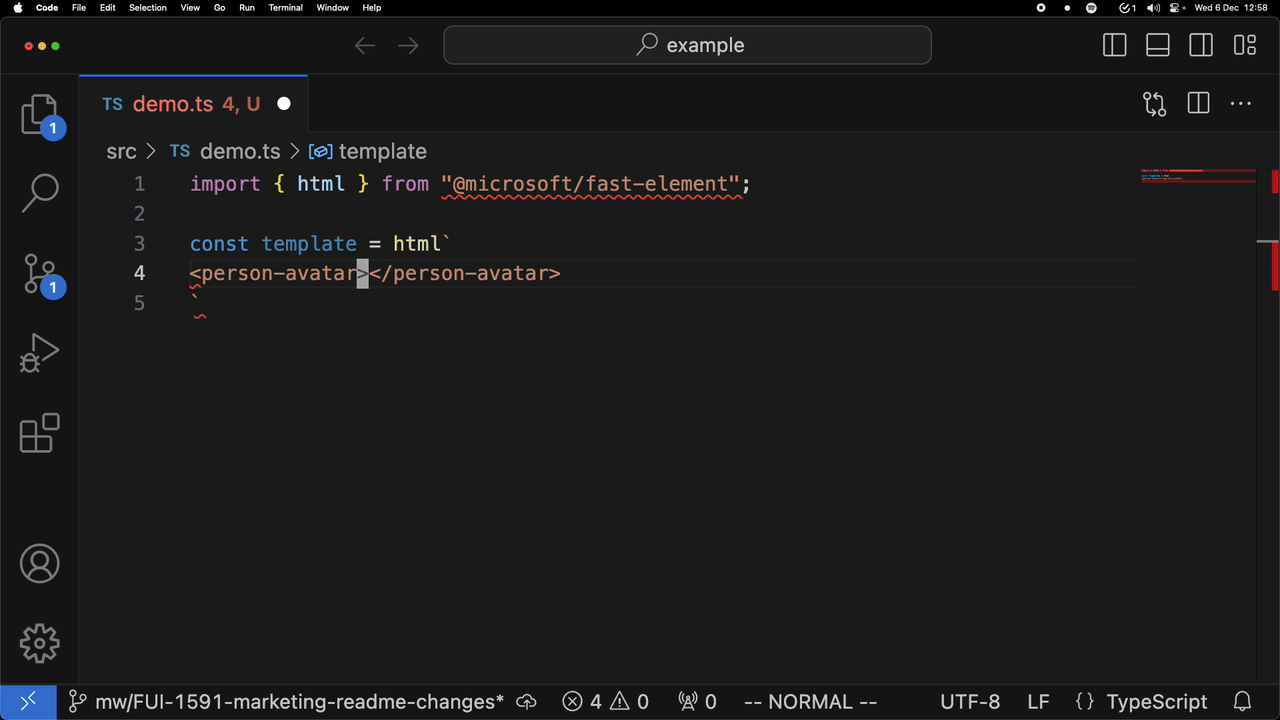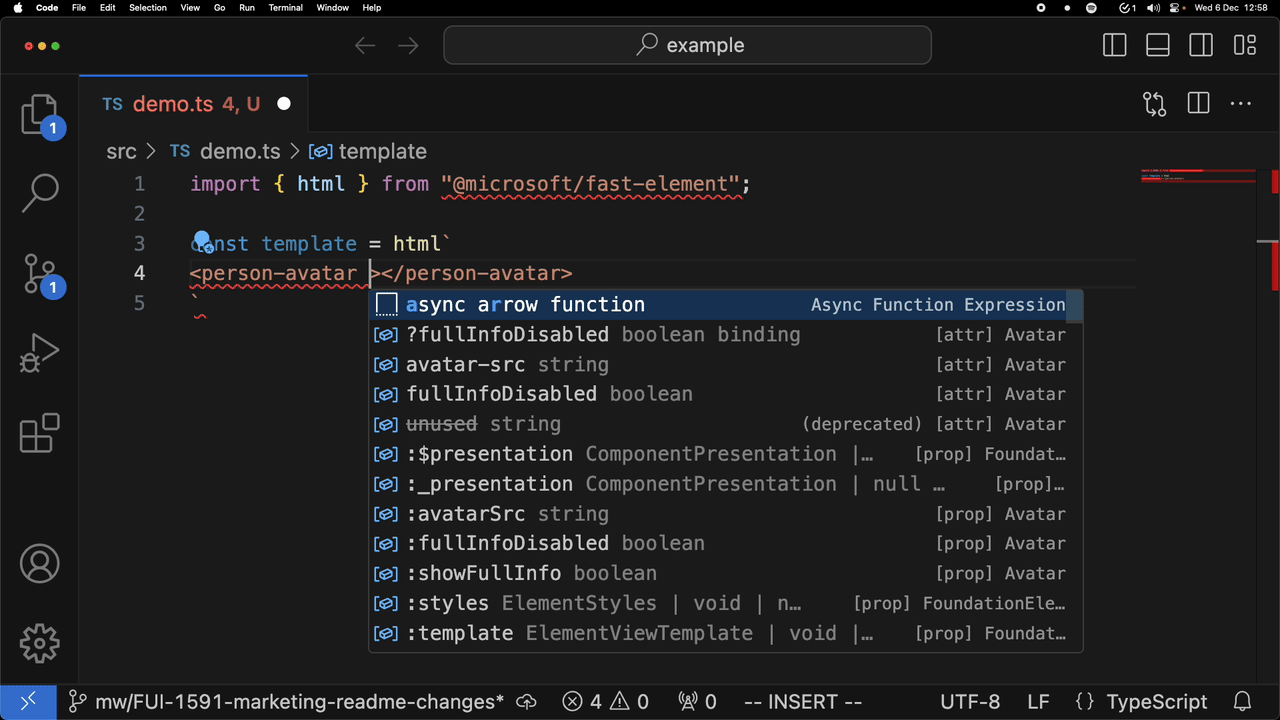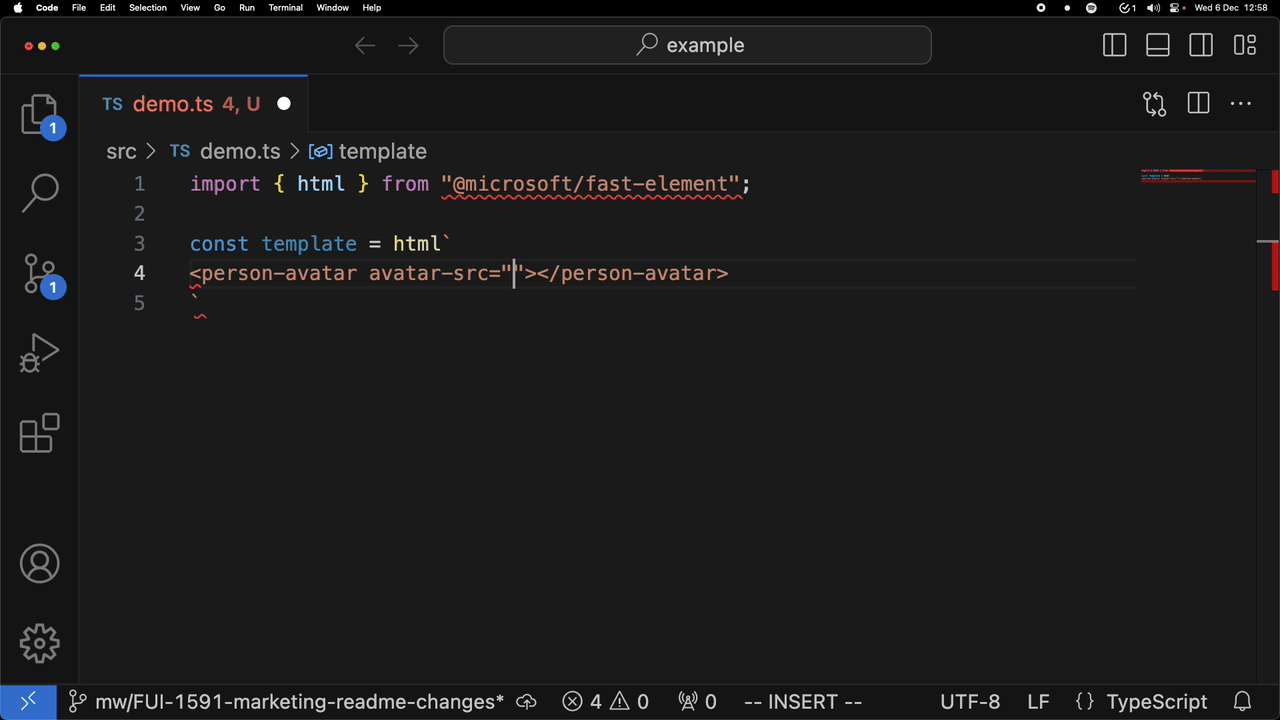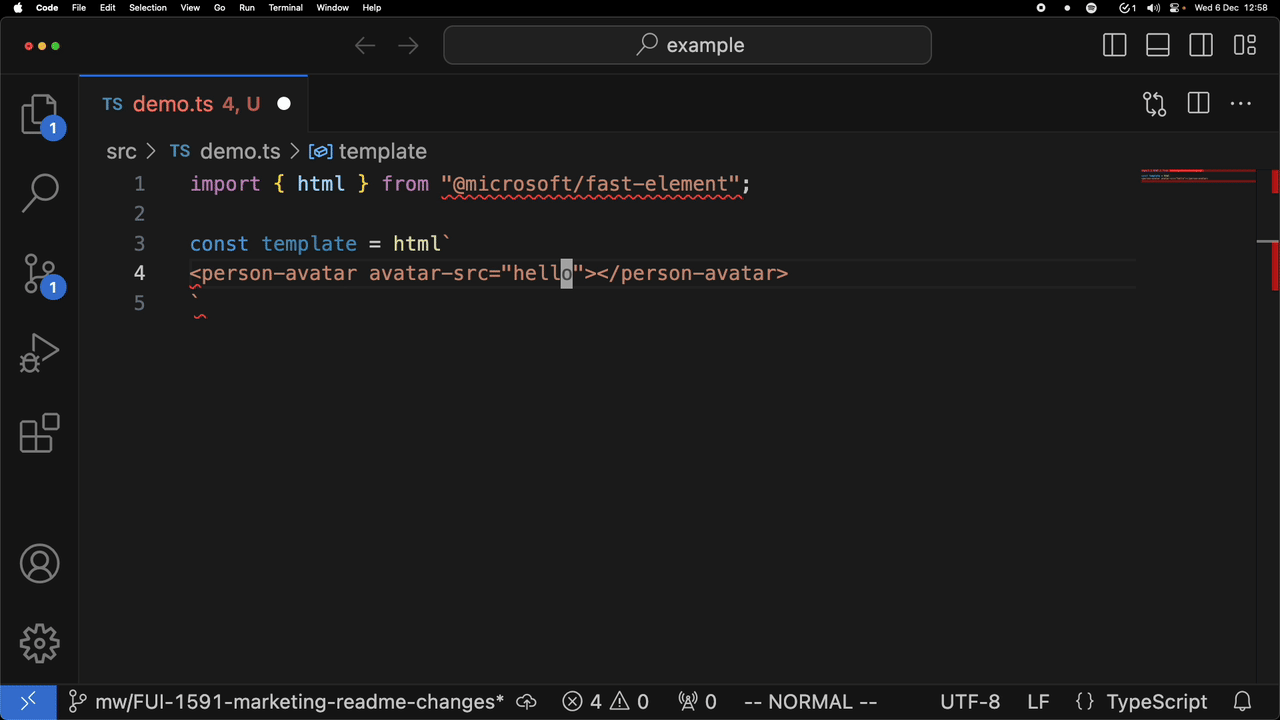
and completion of a custom element:
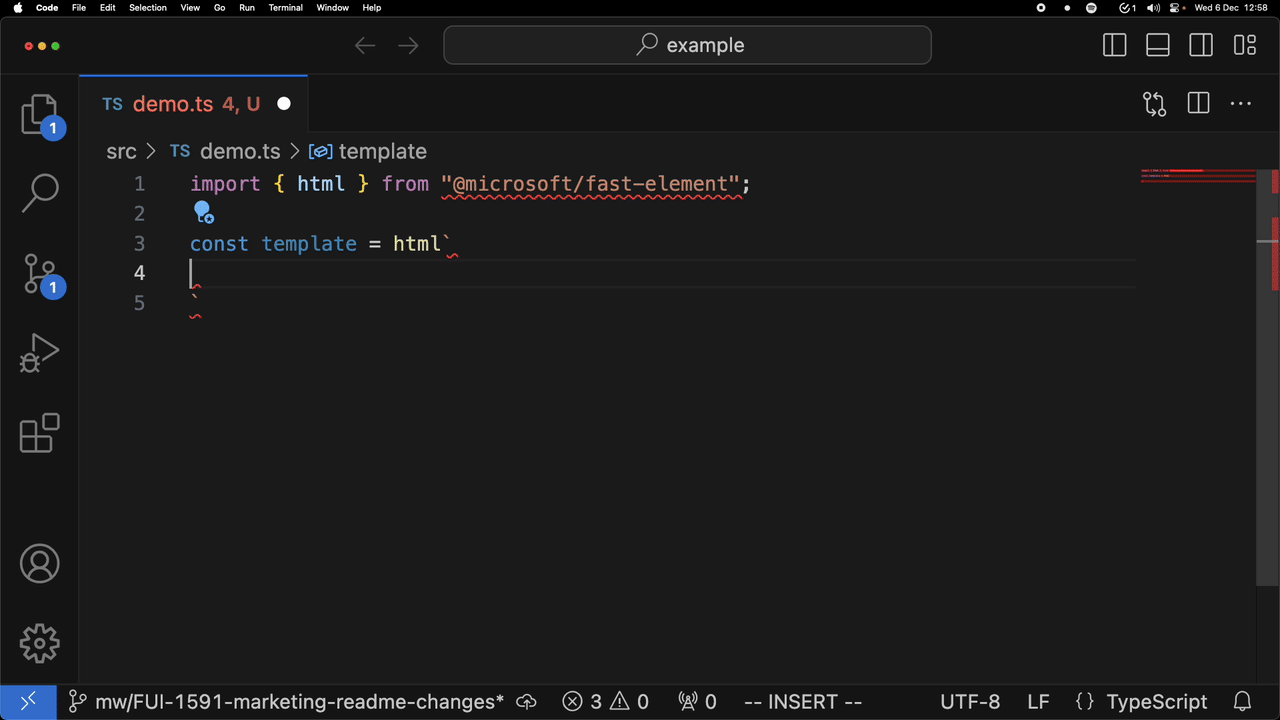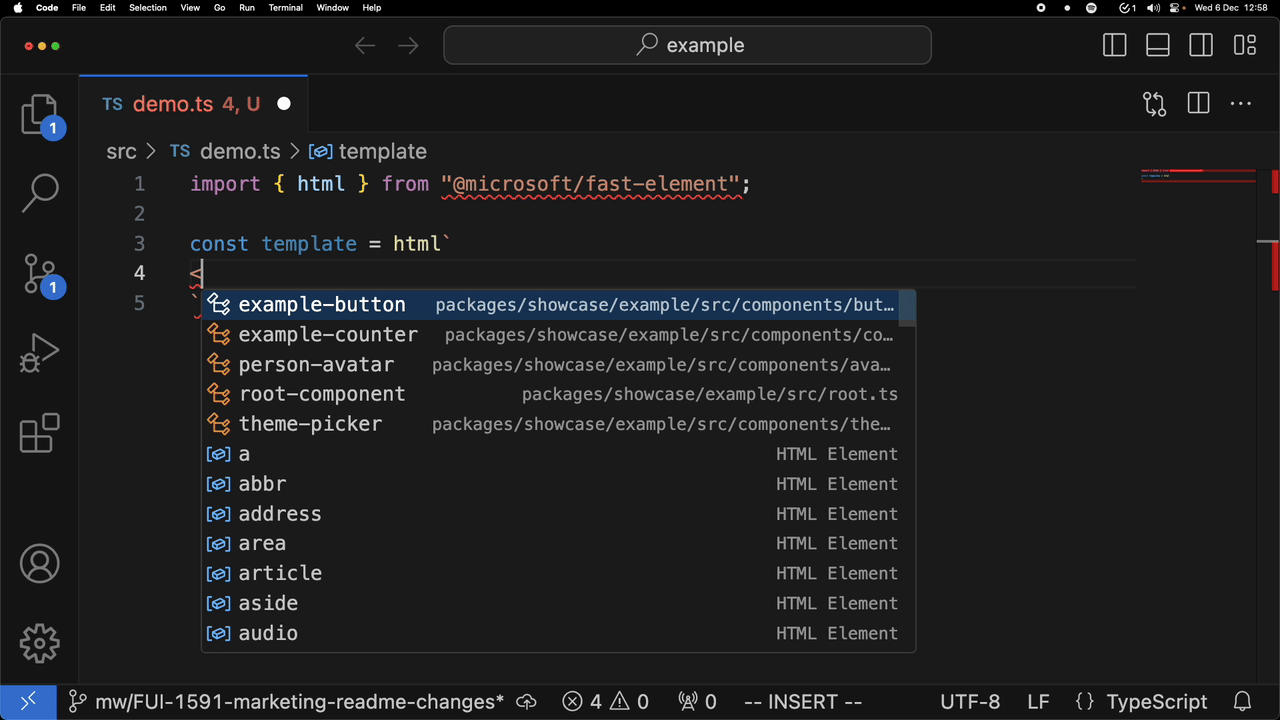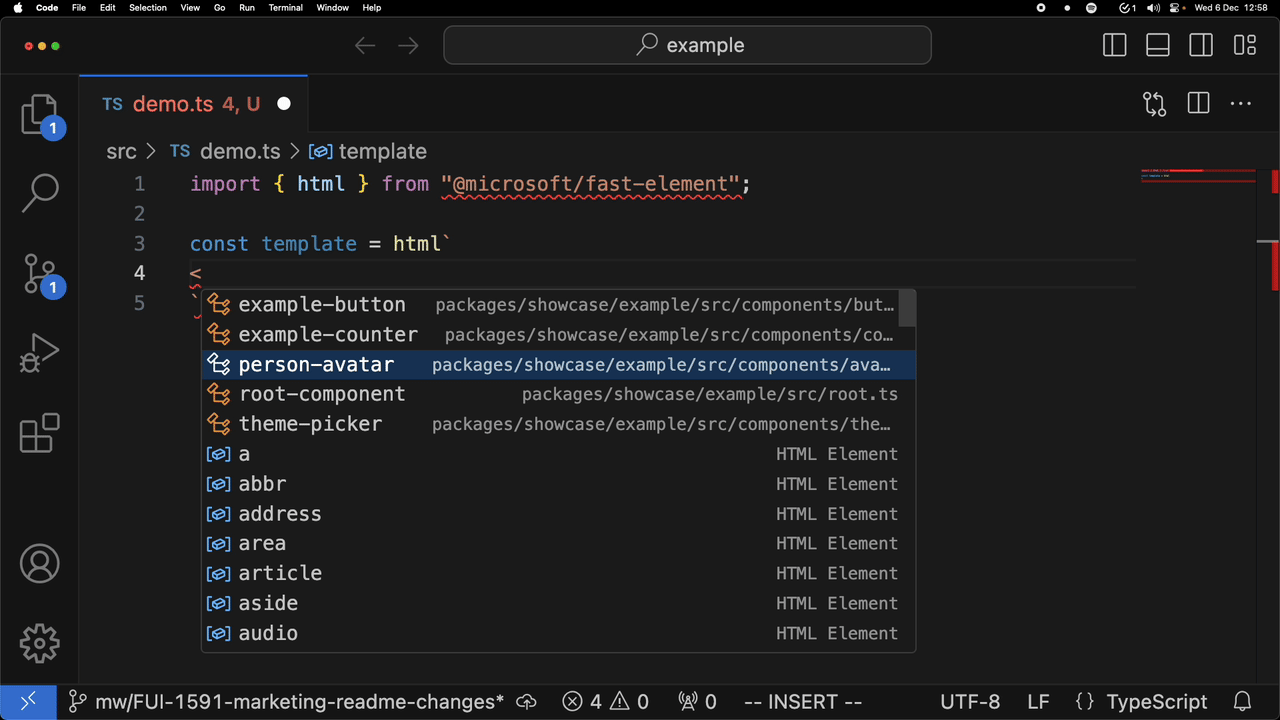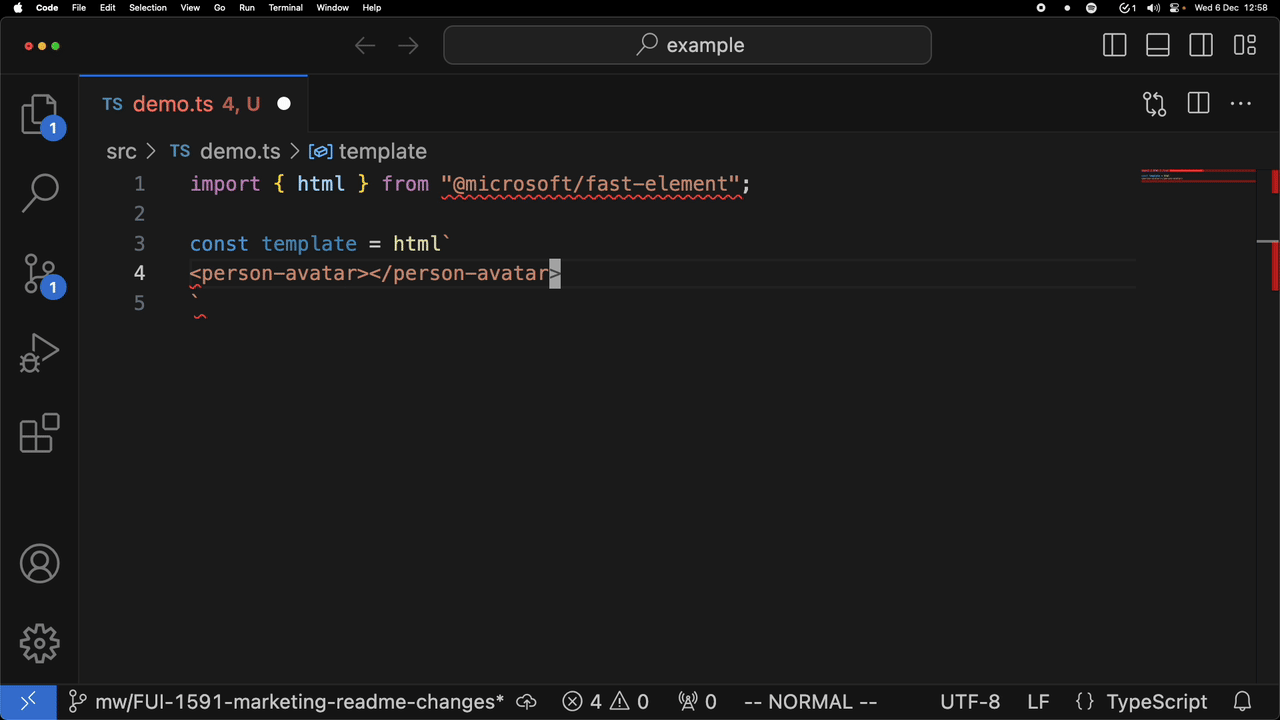
Installing in VSCode
If you created your project using genx or Genesis Create, your dependencies and the initial configuration are done for you automatically. If you created your project from scratch, you must do this as a manual installation.
To start, you need a Genesis project and foundation UI installed in your node_modules (this is enabled by default for all generated projects).
-
Configure your VSCode to use your local typescript install (by default it uses the version of typescript it is bundled with).
- Create a new directory called
.vscode. - In this directory, create a new file called
settings.jsonand paste in the block below:
- Create a new directory called
{
"typescript.tsdk": "node_modules/typescript/lib"
}
- To pick up this configuration. Close and restart VSCode. You must run it from
.vscodedirectory that you have just created.
-
Check that the plugin is working.
- Open any typeScript file.
- Open the command palette: SHIFT+CTRL+P (or SHIFT+COMMAND+P on a Mac).
- Click in the top bar of VSCode and select
TypeScript Version.
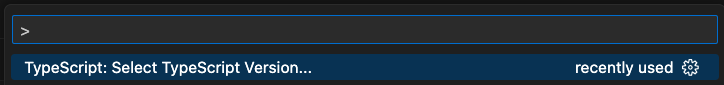
- Then select
Use Workspace Version.
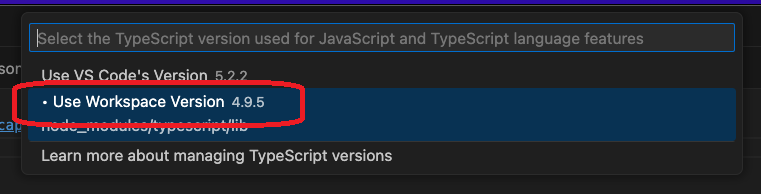
From now on, when you make any changes to the file, you can see all the features of the plugin: errors, warnings and completions on the components that are local to the project.
Installing in IntelliJ
JetBrains IDEs, such as IntelliJ, only have partial support for the LSP. The data files generated for the LSP enhance completion functionality, and the LSP will provide diagnostics. However, Quickinfo functionality (such as jumping to definition) is not supported.
If you created your project using genx or Genesis Create, your dependencies and the initial configuration are done for you automatically. If you created your project from scratch, you must do this as a manual installation.
To start, you need a Genesis project and a local npm project in a lib directory.
-
Launch the IDE with the project at the root of the monorepo.
-
Go to
Settings -> Preferences -
Navigate to the
Typescriptsettings in theLanguages & Frameworkssettings.- Check that the
TypeScriptoption is set to thenode_modules/typescriptof your local project (as shown below). If it is not set correctly, change it. - Enable the
TypeScript Language Servicesettings, as shown below.
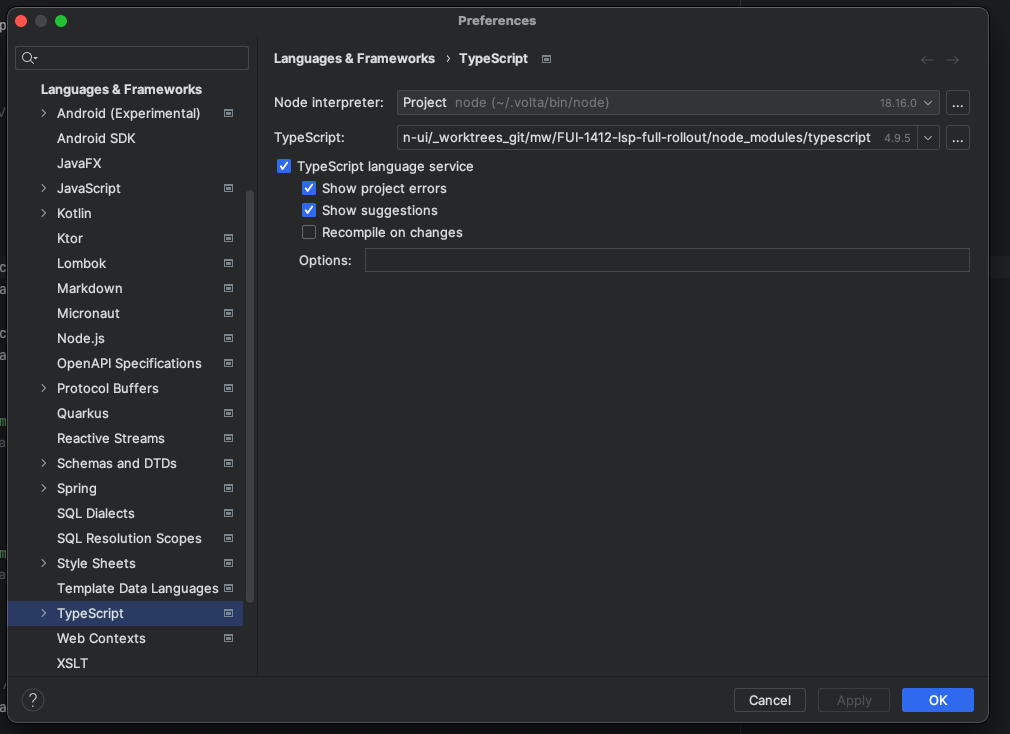
- Check that the
Manual installation
If your project was not created using either Genesis Create or Genx, there are two extra steps you need to make before you configure your IDE.
To start, you need your Genesis project open in your IDE and a local npm project in a lib directory.
- Add the dependencies
In your project's
srcfolder, save the custom elements LSP and the Genesis plugin as dev dependencies.
npm i --save-dev @genesiscommunitysuccess/custom-elements-lsp @genesiscommunitysuccess/cep/fast-plugin
-
Configure your
tsconfig.jsonfile- Open VSCode and navigate to the
tsconfig.jsonfile. - Copy the
pluginsblock shown below.
- Open VSCode and navigate to the
{
"compilerOptions": {
"plugins": [
{
"name": "@genesiscommunitysuccess/custom-elements-lsp",
"srcRouteFromTSServer": "../../..",
"designSystemPrefix": "rapid",
"parser": {
"fastEnable": true,
"timeout": 2000,
"dependencies": [
"node_modules/**/custom-elements.json",
"!**/@custom-elements-manifest/**/*"
]
},
"plugins": ["@genesiscommunitysuccess/cep-fast-plugin"]
}
]
}
}
- The above codeblock provides the default settings that are enabled for a new Genesis project. Unless you have restructured the project manually, this is all you need.
- Edit the codeblock above to match your requirements.
The four main options in the codeblock are:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
name | Mandatory. Set this as @genesiscommunitysuccess/custom-elements-lsp |
srcRootFromTSServer | Mandatory. Set the relative path from the tsserver.js executable in your node modules to your directory with the package.json where the project web root is located. This is likely to be node_modules/typescript/lib/tsserver.js. Default is "../../..". |
designSystemPrefix | Mandatory. Used to work with %%prefix%% to handle components registered as part of a design system. In most cases, new Genesis projects use rapid as the design system. |
plugins | Optional. Use this to set any optional plugins you can add. Specified plugins are applied in order. By default @genesiscommunitysuccess/cep-fast-plugin is enabled to enhance Genesis syntax capabilities. |
If you use a monorepo pattern with workspaces, you must account for potential hoisting of the TypeScript library in the node_modules to a parent directory. If npm has hoisted your typescript install, make sure that you account for this when you set srcRootFromTSServer.
typescript.tdsk must point to the lib directory of the project's typescript install.
The parser options are:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
src | Optional. Set to the glob of the source files in the current project to analyse live. Default is ("src/**/*.{js,ts}) |
timeout | Optional. Time in milliseconds to debounce calls between running the analyser on the source files. The lower the time, the more responsive the LSP will be to changes in the source code - but the more resources it uses. Default is 2000. |
dependencies | Optional. An array of strings of globs that find custom-elements.json from library dependencies to use with the LSP. Libraries will ship production code that the analyser will not be able to parse, so the libraries need to ship the manifest generated from the analyser. An example default you could use to load all files would be ["node_modules/**/custom-elements.json","!**/@custom-elements-manifest/**/*"], which finds all the manifests in your dependencies, but ignores the test manifests from the analyser dependency itself. The default configuration is to enable reading the files supplied from the Genesis UI library. |
fastEnable | Optional. Enables Microsoft FAST parsing of local components, which is the dialect of the Genesis components. You need to enable the plugin for full functionality (enabled by default in the above configuration). |
The parser options control the analysis of the source code to understand semantics, such as whether a custom element has a property or not.
This does not control how the LSP works with the html in the templates to understand whether there are diagnostic issues, or to aid with completion suggestions.
More information
For more information about the plugin, how to set it up, and troubleshooting steps, see the published package on npm.