Genesis Create
Genesis Create enables you to create new financial applications rapidly. Without writing a line of code, you can define a data model, configure the services that run a back end, and set up a complete front end for viewing and interacting with data.
Once you have done that, you can generate the code and then build and run, either in Genesis Cloud Workspace (which provides an IDE to work from), or by downloading and working in your preferred IDE locally.
The code that is generated creates a working app, but you have complete freedom to dive into the code to refine and extend the scope of the app. The generated code includes To Do comments, which you can instantly find and address.
There are two ways of starting Genesis Create:
- Open an existing project from Genesis Launchpad.
- Go to Genesis Launchpad and click "Create with AI".
First steps in Create
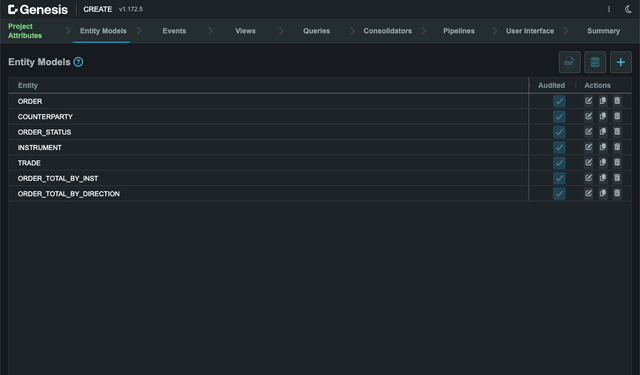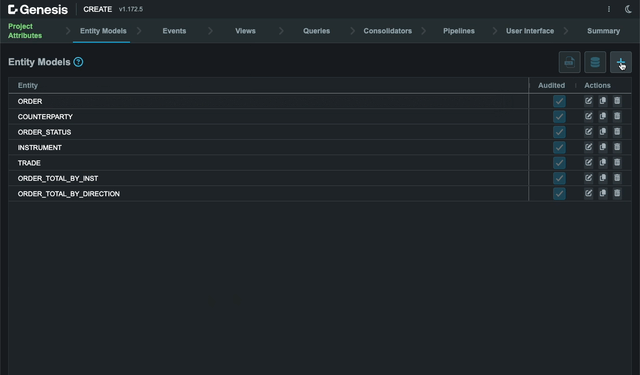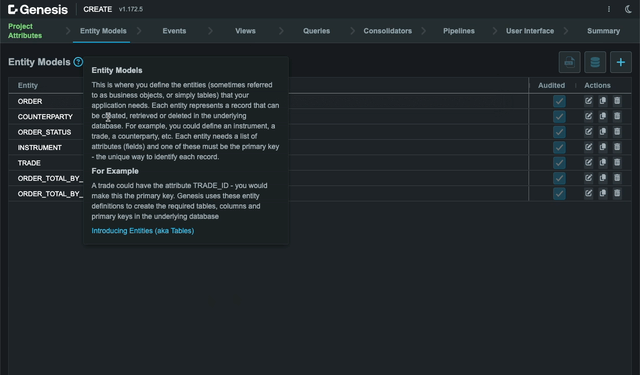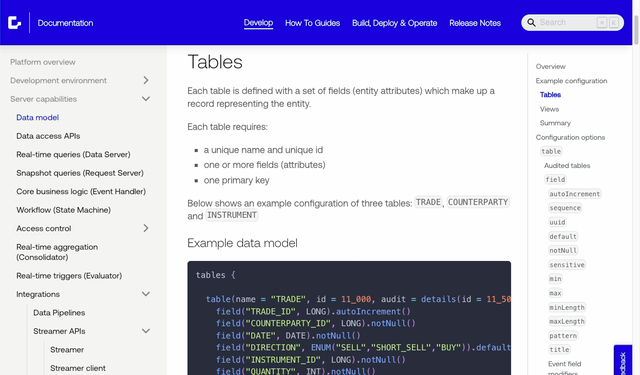
Genesis Create has tooltips throughout. Hover over grid titles, blue buttons and blue question marks to see more details and handy links to documentation.
Genesis Create provides a set of steps that take you through the complete process of setting up a project from which you can generate a working app.
These steps are displayed at the top of the Genesis Create screen.

This section gives you an overview of the key steps to get you started. But note that the number of steps depends on the components you select to use at the beginning of the process. Not all components are covered here.
Project Attributes
The first step is to name your project and select the Genesis components that you need.
- Give your project a usable name. This will be used in the file names, so keep it short and practical, and do not use spaces.
- Provide a description of the project, which will become the README file. Markdown formatting is supported.
- Select the components that you want to include in your application (in addition to the mandatory components). To add a component, click on the
Add Genesis Componentsbutton at the top right.
Selected Components
A Genesis application is built from a set of components that have different purposes. The components you have selected are listed in the Selected Components area.
Note that Base Genesis Server and User Authorization are mandatory.
You need to give some thought to your requirements at this point. Click on Add Genesis Components and take a look at what is available.
You almost certainly want to select Real Time Queries. This makes data from your database available to the front end.
If you want to consume data from another system or to publish data from this application to another system, select Data Pipelines.
When you have finished, click on the Next button at the bottom right of the window to go to the next step.
Entity Models
In this step, you define the entities for your application. An entity is essentially a table that can contain records. For example, you could define a counterparty, a trade, a currency, and so on.
Each entity needs a list of attributes (fields), and one of these must be the primary key - the unique way of identifying each record in the table. So, your COUNTERPARTY entity might need an automatically-generated unique ID (which would make a good primary key) as the first attribute. You could then add attributes such as COUNTERPARTY_LONG_NAME, COUNTERPARTY_SHORT_NAME, and so on.
Creating a new entity
To define an entity, click on the New Entity button at the top right. In the screen displayed:
- Type a name for the entity and click on
Save. All characters are converted to caps and all spaces are converted to underscore. - Optionally, you can click to set two things:
•
Generate Audit Trailsets automatic auditing of every change to the table. •Enable right codescreates codes that control view and update access to this table. You can edit the default codes, if required. - To add the attributes for the entity, make sure that the
New Attributespanel is displayed on the right (select theAttributestab in the main area if necessary).
Adding attributes to an entity
For each attribute that you want to add, make sure that the New Attributes panel is displayed. First, let's look at adding a primitive - a standard type of data, such as STRING or INTEGER.
- Make sure that the
Primitivebutton is selected. - Select the
Typeof data (STRING, INTEGER, BOOLEAN, etc). This controls the other fields available for that type. - Enter a unique name for the field.
- Enter or select any other relevant values in the panel, such as default values. In the example below, we are adding an attribute called CURRENCY_ID of type STRING.
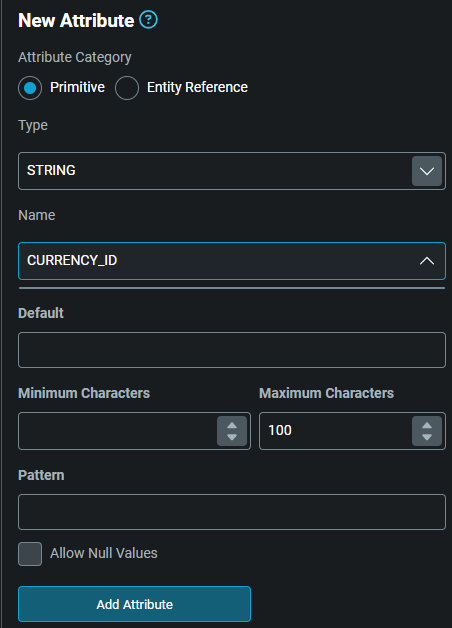
- Click on the
Add Attributebutton. This adds the attribute to the list in the main area.
Primary key
The primary key is the default way to find records in an entity. Every entity has to have a primary key.
When the attributes for your entity are listed in the main area, you can set the primary key for the entity. Select the Primary Key checkbox for the relevant attribute(s) to make the record unique. If yu want to select multiple fields (to create a multi-field key), the ordering your of the selected attributes is important. You can re-order by clicking the symbol on the far right and dragging your attributes.
Here, we have selected CURRENCY ID as the primary key. We have also set Generated so that the value of this attribute is generated automatically. Each new record submitted will have a unique sequential integer for this field, prefixed with the letters CU.
Note that edit and delete buttons are available to the right of each attribute in the list, so you can go back and change any attribute you have already set up.
Indices
An index gives you extra ways of searching for records on the entity. For example, users might want to find trades by instrument or by currency symbol.
Indices can be unique, which enables you to find a single record or non-unique, which enables you to find a range of records.
To add an index to the entity that you are creating or editing:
- Click on the
Indicestab to view the indices for the entity. - A delete button is displayed to the right of each index (except the primary key, which cannot be deleted).
- Use the
New Index panelto add a new index.- You can select one or more fields for the search, depending on the attributes in the entity.
- use the
Typefield to make the index unique or non-unique. - A default name for the index is displayed in the
Namefield. You can change this, if necessary. - When ready, click
Add index. The new index is listed in the main area under theIndicestab.
- When you have finished, click on the
Donebutton to return to the Entity Models screen, where all your entities are listed.
Entity references
Entity references are useful, because they enable you to add attributes from different entities to create views. You can select another entity as a reference, and then you will be able to add fields from that entity to create a view later on.
You must have at least one entity reference in a view if you want to be able to create a view from that entity
To create a reference to another entity:
-
In the
New Attributepanel for your entity (when you are creating or editing a new entity), click on theEntity Referencebutton. -
Click at the end of the
Typefield. The dropdown list includes all the entities that you can refer to.
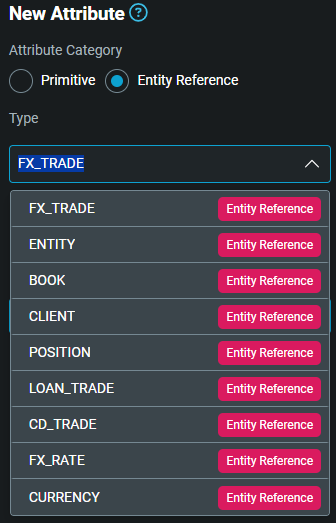
-
Select the relevant entity. The primary key of that table is displayed for information.
-
Click on the
Add referencesbutton. This displays the reference in your list of attributes.
Once you have added all the attributes to your entity, click on the Done button to return to the main area, where all your entities are listed.
You have the chance to set right codes at many points in Genesis Create. These codes enable you to control which users have access to items in the database. They give you a great deal of flexibility in controlling access.
We strongly recommend that you use these.
Creating a data model from Excel
You can create a data model with entities (tables) and views directly from an Excel workbook.
In the Entities main screen, click on the Detect From Excel button. This enables you to select a spreadsheet.
If you already have an entity model in Genesis Create, this button is not available. It becomes available if you delete all the entities in your current project.
Alternatively, clear the current entity model and start a new project. Click on the three dots at the top right of the window and select New. You are warned that this clears any current changes. If necessary, cancel, then click on the three dots again and select Save. This downloads the project as a JSON file.
When you select this button, Genesis Create attempts to create a data model from the workbook that you have selected. If it is successful, it displays information about the data model it has created. For example, here it has created three entities and one view.
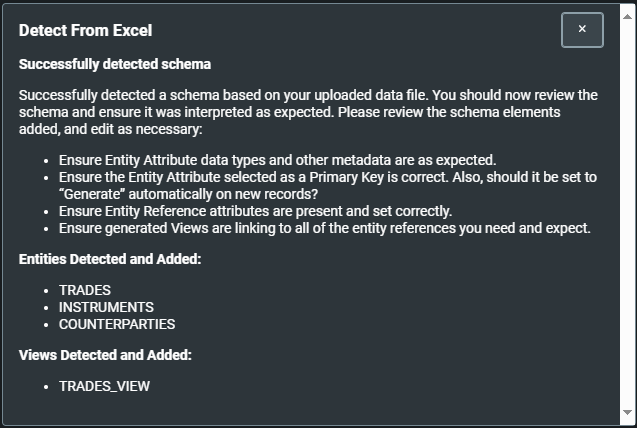
Once you have closed the dialog, you can see the details of the entities and views that have been produced, and you can work your way through the rest of the steps in Genesis Create to complete the project.
Adjusting an Excel workbook
The real world is messy, and Genesis Create will not be able to extract a perfect data model from every workbook that you select. However, if you know the general rules for how the extraction process works, you can adjust your workbook and try again.
The transformation process follows these rules:
- The size of the Excel file must not be larger than 10MB.
- Each tab (worksheet) needs to become a single entity or view. Hidden sheets are ignored.
- Row 1 contains the column headings, which become the attribute names. All attribute names are in caps, with spaces turned into underscore characters. So,
Account namebecomesACCOUNT_NAME, for example. Illegal characters, such as%are converted automatically. - The data for the entity begins at row 2. The data in each column determines the type of the attribute (in row 1). Where the process cannot determine a type, it defaults to STRING. The data in each worksheet is saved in a separate CSV file.
- Column A is used as the primary key for the entity (or root entity of the view).
- A column attribute is ignored if it has no data in any rows.
- Where a column is formatted as Excel Date type, the values for all rows in the column must be formatted properly and compliant with the specified date format.
- If any column in an Excel sheet has a datetime value, this is converted to DATE type in the format yyyy-MM-dd.
- Entity references are created (and used to set up views) where a worksheet contains a VLOOKUP that looks at a column on the same sheet, and looks up a dataset looked on a different sheet.
It is essential to look carefully at your workbook and adjust it to suit these rules. The more you can adjust the workbook to fit these rules, the better the resulting schema is likely to be. It will also make it easier for you to extract the data and reload it into your generated app.
- In particular, make sure that the attribute that you want to be the primary key is in column A.
- It is worth adjusting the data in row 1 so that this produces meaningful attribute names. In particular, you should avoid long names.
Extracting the data
The data from your workbook is not extracted at this stage. You can extract the data later, after you have generated a project in Create and built the app in Launchpad.
To do this:
-
Copy your Excel file into the folder
server/testData/excel. -
In VSCode, go to the Genesis plugin on the right and select
Tasks -> Scripts -> ExcelData to CSV.
This creates a separate CSV (with the data starting at row 2) file for each worksheet to match the entities and views that have been created.
Completing the application
Once you have adjusted your spreadsheet and you have loaded it successfully (when you load it and Genesis Create responds with Successfully detected schema), you have a set of entities and (where relevant) views. You can proceed through the remaining steps in Genesis Create, then build and run your app.
Finishing adding the entities
When you have finished adding entities, click on the Next button at the bottom right of the window to go to the next step.
Views
Views enable you to display information from more than one table in a single place.
For example, if you want a view of all your trades, you would want the TRADE table (we call that the root entity for the view), but you would add information from the COUNTERPARTY and INSTRUMENT tables as well.
To create a new view, click on the New View button at the top right.
Click at the end of the Root Entity field and select an entity from the dropdown list. This displays a default name for the view in the View Name field.
Underneath, this displays the entities you can join with to create a view. These are listed because your root entity includes entity references to those tables. To join to one of the entities listed:
- Click on the
Selectedcheckbox. - Click on the
Attributestab; you can now see all the attributes for the view, including the attributes from the entity you have joined. - Click on a
Selectedcheckbox for an attribute to add it to or remove it from the view.
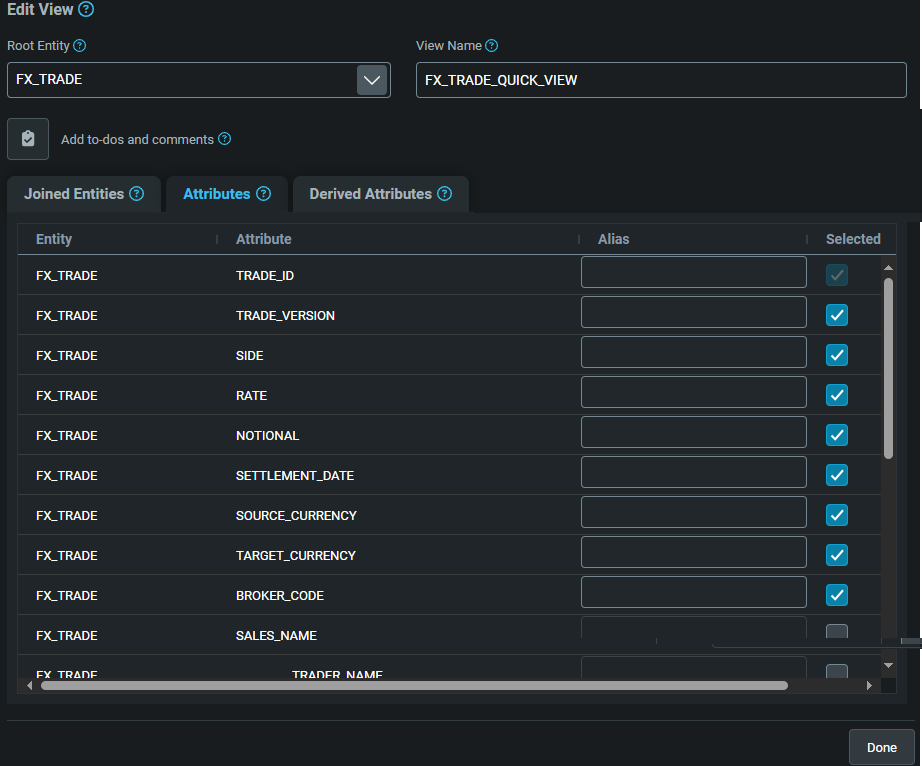
When you have finished, click on Done.
Derived attributes
You can also create derived attributes. These enable you to create a new value from one or more existing attributes. For example, you could divide NOTIONAL attribute by 100 to produce a fee of 1 percent.
To add a derived attribute to the view you are creating or editing:
- Click on the
Derived Attributestab. - Click on
Add Derived Attribute. - Enter a name for the attribute.
- Select one or more attributes to be used to create the new value.
- In the
Output Typefield, select the data type of the attribute (such as DOUBLE or INT). In the example below, we are creating a derived attribute called FEE of type DOUBLE from two existing attributes.
- Click on
Save and Returnto the main screen for your view. - When you have finished, click on the
Donebutton. This returns you to the list of views.
Finishing views
When you have finished, click on the Next button at the bottom right of the window to move on to the next step.
Queries
Queries make real-time information available to the front end.
At various points, this link enables you to insert TO DO statements and comments that will appear in the generated code. Take time to use this feature; it will save you time later on.
To add a query:
- Click on the
New Querybutton at the top right. - Click at the end of the
Entity or Viewfield and select an entity from the dropdown list. This displays a default name for the view in the Query Name field, which you can change if necessary. - Click on the
Add Querybutton. - This displays all the fields in that entity. You can click to remove any fields you don’t want to include.
- When you have finished, click on
Done. Your new query appears in the list on the Queries page.
After you have added all the queries you need, click on the Next button to move on to the next step.
Consolidators (optional component)
A consolidator can aggregate records in useful ways. It listens to changes to records in a specified entity and aggregates their values into a specified output entity.
For example, it can aggregate Trades into Positions or Orders. Or it can aggregate Payments into Netted Payments.
To add a consolidator:
- Click on the
New Consolidatorbutton at the top right. - Type a name for the consolidator in the
Consolidator Namefield. - To aggregate, you need to select the
Input AttributeandOutput Attributeto group by. The output attribute is determined by the input attribute you select. - Check the fields for configuring the aggregation. The most important field is the
Aggregation Function, which enables you to select the logic for the aggregation, which could be SUM or AVG, for example. (To handle more complex logic, you can customize this in the generated code later on.) When you are happy, make sure that theEnabledcheckbox is set. - Click on
Doneto return to the Consolidators page, where your new consolidator is listed.
When you have finished working with consolidators, click on the Next button at the bottom right to move on to the next step.
User Interface
This step enables you to create the web client for your application.
By default, you are given a main or home page that is the landing page for your app (login is set up for you automatically). You can change the name of the page or add new pages to work with.
In the example below, we have called our landing page FX Blotter. You can create another page by clicking on the + tab next to the page title and supplying a name for the new page.

When you have multiple pages, you can click on the Manage pages link on the right to add, edit and delete pages.
You can build each page by adding tiles. Each tile contains a component, such as a grid display or a chart.
Adding a tile and component
To add a component to a page:
-
Click on
Add Tile. This displays a panel where you can select your components. -
Type a name for the tile. This is used in the code, so keep it short and practical.
-
Scroll through the components in the panel and select the radio button for the one you want, for example,
Real-Time Data Grid + Modifications. Then click onSubmit.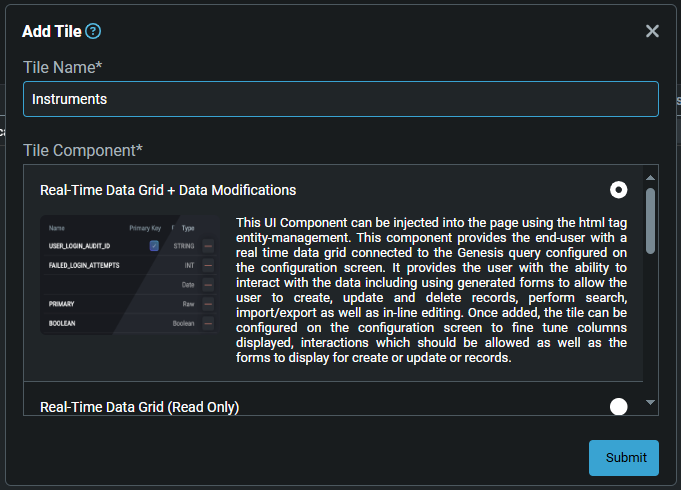
-
The display changes and you need to click on the
Data Sourcefield to select where the data is coming from: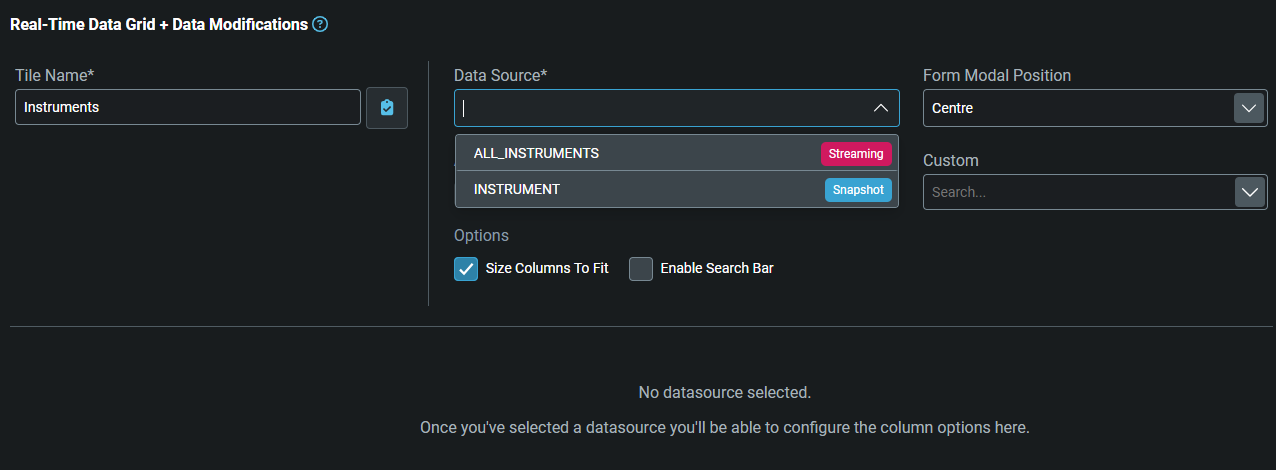
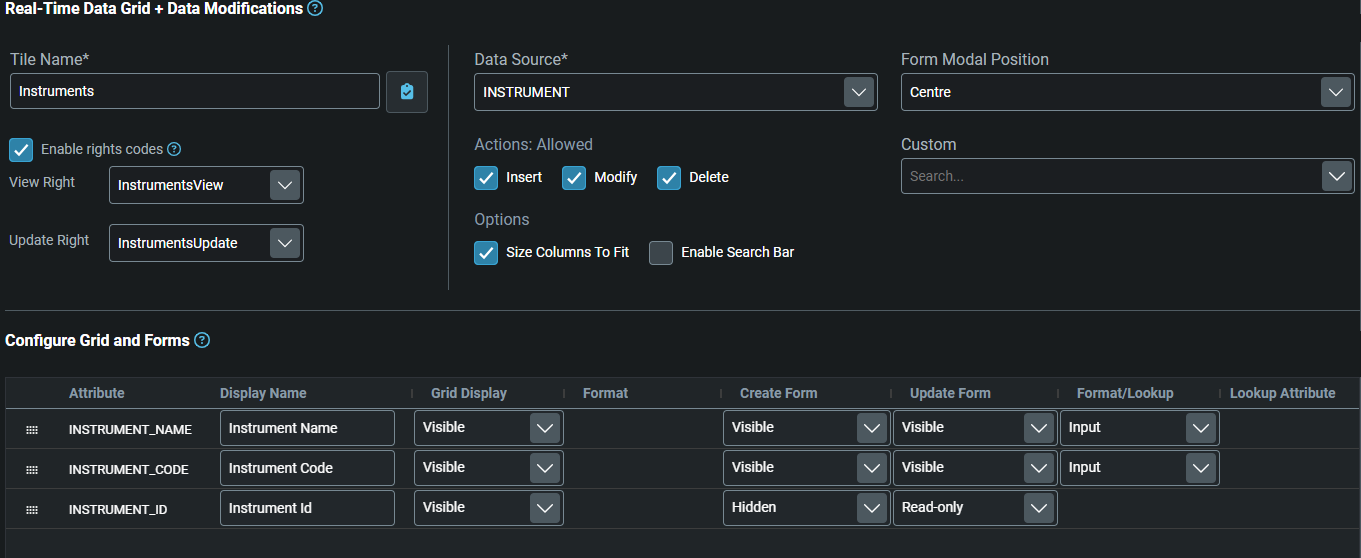
Once you have done this, you can see configuration details for the component you have selected. In this case, you can see the fields (attributes) that will be displayed in the grid and forms for the
Real-Time Data Grid + Modificationscomponent.- The fields for the Grid are on the left.
- The fields for the Insert and Modify forms are on the right.
 tip
tipNote that you can select to hide some or all of the attributes. You can also change the order of fields and the format (such as the number of decimal places).
-
Once you have finished, click on the
Donebutton. This displays the tile and its component in the main list.
Configuring each component
In the main list, there are edit and delete buttons for each tile in the list. There is also a Config column, which shows a red warning triangle if the component needs to be configured.
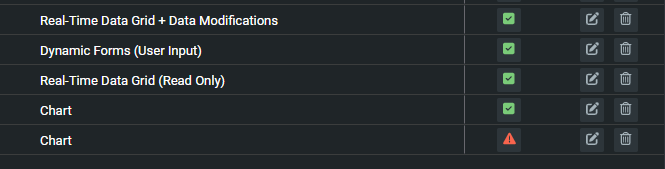
Click on the edit button for the tile. This displays the configuration details for the relevant component in the tile.
Completing the UI
When you have added all the UI components you need, click on the Next button at the bottom right of the window to move on.
Summary
When you reach the Summary page, you have completed the configuration of your project.
The next step is to generate the code so that you can build and deploy.
Opening in your Genesis Workspace
You can now save your project in Genesis Launchpad so that you can build and run in your Genesis Cloud Workspace.
To do this:
-
Click on
Save to Launchpad. This loads your project in Launchpad.
-
After a few seconds, click on the newly displayed button
View in Launchpad. This starts Launchpad and your new project is displayed under the list ofCurrent Projects. From there, you can click to open the project in your Cloud Workspace, where you can build and run without needing to download a development environment.
Downloading your project to run locally
Alternatively, you can download your project to run locally following this guide:
Learn step-by-step
Exclude Gradle Wrapper JAR
By default, your generated project includes a JAR file so that you don't need to have the Gradle build tool available locally. Some institutions block these JAR files. If this affects you, make sure that Exclude Gradle Wrapper JAR is set to exclude the JAR. After you have unzipped your project, you must then install gradle manually following these instructions.
For the instructions below, change {URL} to be either:
- Your company's internal gradle distribution url for gradle 8.3+
- The public URL https://services.gradle.org/distributions/gradle-8.3-all.zip
If your local Gradle installation version is 8.3+ or 7.6.4+, you can simply run gradle wrapper --gradle-distribution-url={URL} at the project root level. If you don't have this, else if you receive errors, follow these instructions:
-
Download the Gradle zip distribution manually from
{URL}and unzip it. -
Run the following command in your project's root directory. The command assumes you unzipped the gradle download in
~/Downloadsand this part of the command should be changed accordingly if you are using another directory:- Windows
- Mac OSX / Linux
~\Downloads\gradle-8.3\bin\gradle.bat wrapper --gradle-distribution-url={URL}~/Downloads/gradle-8.3/bin/gradle wrapper --gradle-distribution-url={URL}